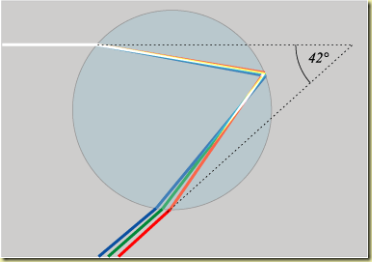
The dispersion of the light is something very simple to obtain. You only need a glass prism to be able to separate the different radiations of the white light while passing through the crystal because each radiation has its own speed.
The red light is the fastest, followed by the orange, the yellow, the green, the blue, the indigo and the violet.
The explanation is that the red light has the longest wave length, and the refraction index is minor, at the time it is less refracted and the refraction angle is lightly major.
The violet light has a complete different result: its wave length is shorter, and the refraction index is major. Therefore it is refracted more and its refraction angle is the smallest, turning a major angle aside that other visible lights.
This is reflected in Snell's refraction law: the lights of different colors spread in the material medium at different speeds; only in the vacuum they propagate at the same speed.
During the rain, the air has water drops in it, and when the light passes through it the colors of the visible spectrum appear. The red light appears in the outside and the violet in the inside.
If there is much light, it could be possible to perceive the second rainbow. Due to a second reflection of the light inside the drops, obviously, the order or the resulting colors will be reversed with the reversed colors reversed.
When the light comes into the water drop a refraction is produced. After that a reflexion is produced inside the drop, and later there are two refractions, one from the inside the other in the outside.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario